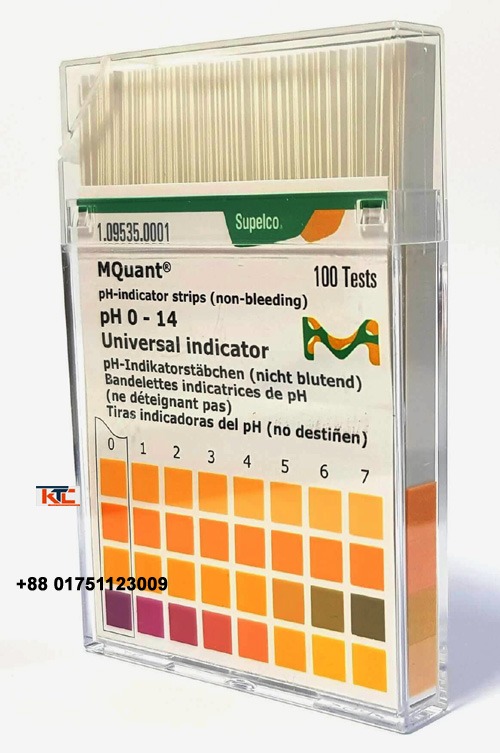
Ph indicator paper
৳ 1,200.00
ph indicator paper often simply called pH paper or litmus paper (though litmus is a specific type), is a
100 in stock
Brand =Germany
ph indicator paper:
The Best ph indicator paper
often simply called pH paper or litmus paper (though litmus is a specific type), is a simple and inexpensive tool used to determine the acidity or alkalinity of a liquid solution. It’s essentially a strip of paper that has been impregnated with one or more chemical compounds known as pH indicators.
What is pH indicator paper?
Before diving into how the paper works, it’s important to understand pH. pH is a scale (typically from 0 to 14) that measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H$^+$) in a solution:
pH 7 is neutral (e.g., pure water).
pH less than 7 indicates an acidic solution (higher concentration of H$^+$ ions). The lower the number, the more acidic it is.
pH greater than 7 indicates a basic (or alkaline) solution (lower concentration of H$^+$ ions and higher concentration of hydroxide ions, OH$^-$). The higher the number, the more basic it is.
How pH Indicator Paper Works: The Chemistry
The magic of pH paper lies in the pH indicators it contains. These indicators are usually weak acids or weak bases that exhibit different colors depending on the pH of the solution they are in.
Our Best ph indicator paper basic mechanism:
- Indicator Molecules: pH indicator molecules (let’s call the acidic form “HInd” and its conjugate base “Ind$^-“)existinanequilibriuminwater:HInd(aq)+H_2$O (l) $\rightleftharpoons$ H$_3O^+$ (aq) + Ind$^-$ (aq)
Color Change:
- In an acidic solution (high H$_3O^+$ concentration): According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, the equilibrium will shift to the left, favoring the HInd form of the indicator. The HInd form has one specific color.
In a basic solution (low H$_3O^+$ concentration, high OH$^-$ concentration which consumes H$_3O^+$): The equilibrium will shift to the right, favoring the Ind$^-$ form of the indicator. The Ind$^-$ form has a different specific color.
At neutral pH or within an intermediate range: Both forms may be present in significant amounts, resulting in a mixed or intermediate color.
Universal Indicators: Most pH indicator papers that cover a wide range (like 0-14) are actually coated with a mixture of several different indicator dyes. Each of these dyes changes color at a different specific pH range. By combining them, the paper can exhibit a wide spectrum of colors across the entire pH scale. This allows for a more granular estimation of pH.

How to Use pH Indicator Paper:
The process is very straightforward:
- Get a strip: Tear or cut a small strip of pH indicator paper.
- Dip it: Dip one end of the pH paper into the liquid you want to test. You only need to wet it for a second or two; don’t soak it for too long.
- Observe the color change: The paper will immediately change color (or within a few seconds, depending on the type).
- Compare to a color chart: Most pH paper comes with a color chart printed on its packaging. This chart shows various colors corresponding to different pH values (e.g., red for strong acid, orange/yellow for weak acid, green for neutral, blue for weak base, purple/violet for strong base).
Advantages and Limitations:
Advantages:
- Simple and Easy to Use: Requires no special training or equipment.
- Inexpensive: Much cheaper than electronic pH meters.
Portable: Easy to carry and use in the field.
- Quick Results: Provides an instant indication of pH.
- Less Precise: pH paper provides an estimation of pH, typically to the nearest whole number or half-number. It’s not as accurate a digital pH meter, which can give readings to two decimal places.
- Subjective Reading: Color perception can vary between individuals, leading to slight variations in reading.
- Not for Gases or Solids: Primarily designed for testing liquids.
Despite its limitations, pH indicator paper is an invaluable tool for quick, qualitative pH assessment in education, basic laboratory work, gardening, and various household applications.
Be the first to review “Ph indicator paper”
You must be logged in to post a review.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.